Skin Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, Treatments and What You Need To Know!
17 Aug 2023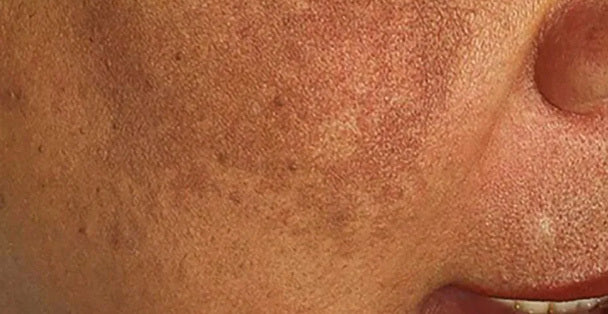
Introduction
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to the darkening of certain areas of the skin, leading to uneven skin tone and discoloration. This blog will delve into the various aspects of hyperpigmentation, including its core definition, the different types for various skin tones, its causes, and how it manifests. Moreover, we will explore effective ways to deal with hyperpigmentation, highlighting skincare essentials that have proven to be helpful in addressing this concern.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition characterized by the excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for determining our skin color. When there is an overproduction of melanin in certain areas, it leads to the appearance of dark spots or patches on the skin, which can be of various shapes and sizes.
Hyperpigmentation for Different Types of Skin
Hyperpigmentation can occur differently based on an individual's skin type and color. The most common types are:
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH):
This type of hyperpigmentation occurs after inflammation or injury to the skin. It often appears as dark spots or patches after conditions like acne, eczema, or any physical trauma to the skin. People with medium to dark skin tones are more prone to PIH.
Melasma:
Melasma is another form of hyperpigmentation that affects mainly women, particularly those with darker skin. It is often triggered by hormonal changes. Melasma typically presents as larger, symmetrical dark patches on the face.
Sunspots or Solar Lentigines:
Sunspots, also known as age spots or liver spots, are a result of sun exposure over time. They are common in individuals with fair skin and usually appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation and How it Looks Like
The overproduction of melanin, which causes hyperpigmentation, can be triggered by various factors:
Sun Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun stimulates the melanocytes to produce more melanin, leading to sunspots or freckles.
Hormonal Changes:
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy, menopause, or the use of certain pills, can trigger melasma.
Skin Inflammation:
Any form of skin injury, including acne, cuts, or burns, can result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Genetics:
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to develop hyperpigmentation, making them more susceptible to dark spots or patches.
Age:
As we age, our skin becomes more susceptible to hyperpigmentation due to a decrease in skin cell turnover and increased exposure to environmental factors.
Hyperpigmentation can occur in various ways depending on the type and severity. It may appear as small, dark spots or larger, patchy areas that can vary in color from light brown to deep black. The affected areas often have a well-defined border, making them distinguishable from the surrounding skin.
How to Deal with Hyperpigmentation
Dealing with hyperpigmentation requires a comprehensive approach that includes both prevention and treatment. Here are some effective strategies:
Sun Protection:
One of the most crucial steps in managing hyperpigmentation is to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Regularly use a broad-spectrum sunscreen lotion with a minimum SPF of 30, even on cloudy days, and reapply every two hours when outdoors.
Topical Treatments:
There are several products available that can help fade hyperpigmentation. Look for ingredients like hydroquinone, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), kojic acid, vitamin C, niacinamide, and retinoids, as they are known for their skin-brightening and exfoliating properties.
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels performed by a dermatologist can effectively reduce hyperpigmentation by removing the top layers of the skin, revealing a fresher, more even-toned complexion.
Laser Treatments:
In more severe cases of hyperpigmentation, laser therapies can target and break down the excess melanin, promoting a more balanced skin tone.
Skincare Routine:
Adopt a consistent skincare routine that includes cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing. Be gentle with your skin and avoid picking at blemishes, as it can worsen hyperpigmentation.
Products to Help with Hyperpigmentation
In the quest to combat hyperpigmentation, several products have proven to be beneficial:
Vitamin C Serums:
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that can help improve the skin’s glow and fade dark spots. Vitamin C serum proves to be beneficial in targeting hyperpigmentation.
Niacinamide:
Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, in skincare can effectively reduce hyperpigmentation and improve overall skin texture. The Coffee Body Mask with Niacinamide is a great addition to de-tan and de-pigment.
Retinoids:
These derivatives of vitamin A accelerate cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots and promote a more even skin tone.
Retinoids:
These derivatives of vitamin A accelerate cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots and promote a more even skin tone.
Hydroquinone Creams:
Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production, making it effective for treating hyperpigmentation.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that affects people of all skin types and colors. Understanding the causes and types of hyperpigmentation is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan. By integrating sun protection, topical treatments, and other therapies into your skincare routine, you can effectively treat hyperpigmentation and achieve a more radiant, even-toned skin.
FAQs
1. What makes hyperpigmentation worse?
Sun exposure is a significant factor that can worsen hyperpigmentation. UV rays trigger the production of melanin, leading to darker spots and patches.
Picking at blemishes or skin injuries can also exacerbate post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
2. Is hyperpigmentation a permanent condition?
In many cases, hyperpigmentation can fade over time, especially with the use of appropriate skincare products and treatments. However, some types, such as melasma, may be more challenging to treat and require ongoing management.
3. Which SPF sunscreen is best for hyperpigmentation?
When dealing with hyperpigmentation, it's essential to use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. The Green Tea Sunscreen SPF 50 PA++ with Niacinamide is a good pick to protect & repair your skin.
4. What are the side effects of hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation itself is not a side effect but rather a skin condition. However, it can be a consequence of various factors such as sun damage, inflammation, or hormonal changes, which might have their own side effects on the skin.




































































